Advantages and Implementation of ERP Systems for Streamlining Business Operations
Success in today’s fast-paced and fiercely competitive corporate environment depends on remaining organized, efficient, and adaptive. Systems for enterprise resource planning (ERP) have become effective instruments for streamlining operations, improving decision-making, and fostering growth. We will go into the realm of ERP systems in this article, looking at their advantages, methods of implementation, and function in streamlining business operations.
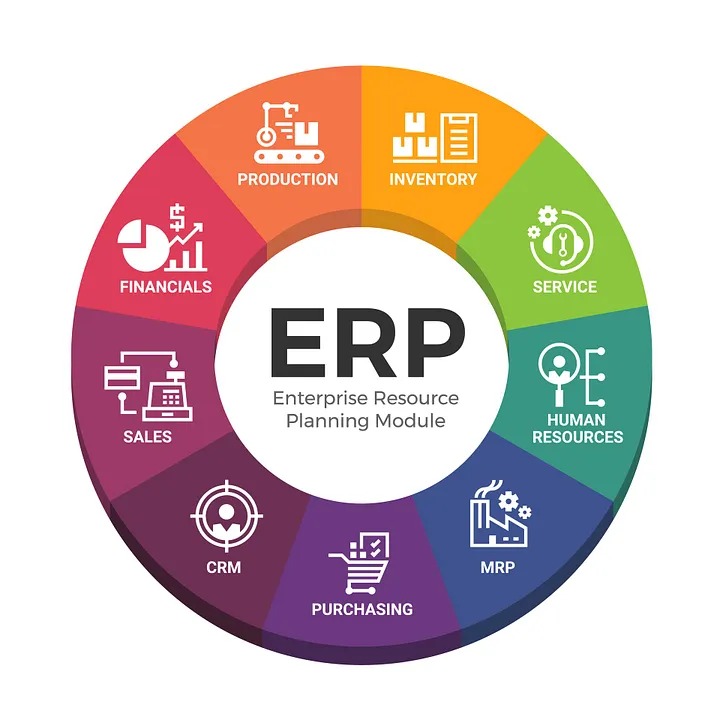
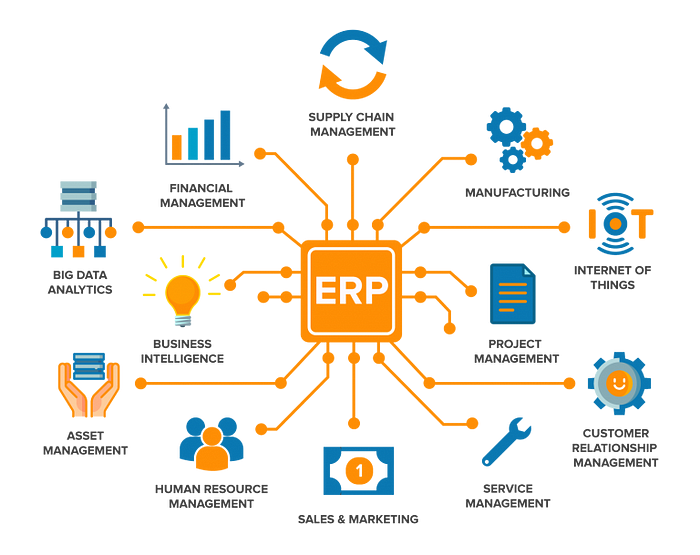
A business’s ability to handle multiple areas of its operations, from finance and human resources to inventory, procurement, customer relationship management (CRM), and more, is made possible by an integrated suite of programs known as an ERP system.
The system offers a central database that enables access and sharing of information amongst departments in real-time, encouraging collaboration and data-driven decision-making.
Key Benefits of ERP Systems Enhanced Efficiency:
ERP systems automate routine tasks, reduce manual data entry, and eliminate duplication of efforts. This leads to improved operational efficiency, reduced errors, and increased productivity across the organization.
Streamlined Processes:
ERP systems foster a constant flow of information by connecting various corporate operations. Process simplification lowers lead times, lessens bottlenecks, and improves customer satisfaction in general.
Making Correct Decisions:
ERP systems give managers instant access to precise and current information, enabling quick and informed choices. This capacity for data analysis helps in trend detection, outcome forecasting, and strategy formulation.
Cost Savings:
ERP systems help in optimizing inventory levels, reducing excess stock, and minimizing production downtime. This leads to cost savings in terms of storage, labor, and procurement.
Improved Customer Relations:
With a comprehensive view of customer interactions and preferences, ERP systems enable personalized communication and better service delivery. This strengthens customer relationships and loyalty.
Regulatory Compliance:
There are stringent regulatory standards for many businesses. ERP systems often come equipped with compliance features that aid in meeting legal standards and reporting obligations.
Implementing an ERP System:
An ERP system implementation is a huge undertaking that needs careful planning and execution. Here is a detailed instruction:
Assessment:
Identify your business needs and challenges. Determine which processes need improvement and prioritize your requirements.
Vendor Selection:
Research and choose a reputable ERP vendor whose system aligns with your industry and business size. Consider components like adaptability, customization choices, and continuous improvements.
Customization:
Tailor the ERP system to match your specific workflows and requirements. This might involve configuring modules, data migration, and integration with existing systems.
Training:
Give comprehensive teaching to your representatives to guarantee they get it how to utilize the ERP framework successfully. This minimizes resistance to alter and maximizes appropriation.
Testing:
Altogether test the ERP framework some time recently going live. Recognize and address any issues to guarantee a smooth move.
Go-Live and Support:
Gradually transition to the new system. Offer continuous support to address any challenges and ensure a successful adoption process.
Conclusion
In a technology-driven era, an ERP system acts as the backbone of efficient business operations. By centralizing data, streamlining processes, and promoting collaboration, ERP systems empower organizations to respond quickly to market changes and drive growth. When implemented thoughtfully, ERP systems have the potential to revolutionize your business, making it more agile, competitive, and ready to embrace the future.
Post a comment